Nvidia is a graphics technology company incorporated in Delaware and headquartered in Santa Clara, California. Founded in 1993, its three co-founders are Jensen Huang, CEO, Chris Malachowsky, and Chris Priem. The firm designs and manufactures graphics processing units and “systems on a chip”, or SoCs. Nvidia has formed several partnerships for advancing the graphics interface, processing of data, and artificial intelligence of self-driving vehicles, and its SoCs are being sold to 320 clients in the automotive industry.
The Nvidia System-on-Chip Technology
Self-driving cars need a lot of information in order to navigate and operate on real-world streets. They also need to be able to rapidly process that information. Nvidia’s SoC for autonomous cars is a system called Xavier. The Xavier is able to process 30 trillion operations per second. The low-powered chip can do this with just 30 watts of power, meaning that it does not drain the vehicle’s battery even while it is collecting and processing so much information. At 15 times faster and more powerful than Nvidia’s previous SoC for autonomous cars, Xavier features more than 9 billion transistors, a custom 8-core central processing unit, a 512-core Volta graphics processing unit, an 8K high-definition resolution video processor, a deep-learning artificial intelligence accelerator, and proprietary microprocessor for computer-vision.
That level of power means that Xavier is able to rapidly collect and analyze information about the road, weather, other vehicles, location, and other key pieces of information that are necessary for navigation in self-driving cars. The chips allow for an artificial intelligence system to conduct deep learning based on the graphics information that it detects and processes. The chips are designed to detect buildings, lane markings on roads, roadside signs, curves in the road, and other information that self-driving cars would need for safe navigation. Nvidia’s technology also offers self-parking, end-to-end high-definition mapping, driver assist, and automated highway driving capabilities.
Testing of Nvidia Technology in Autonomous Cars
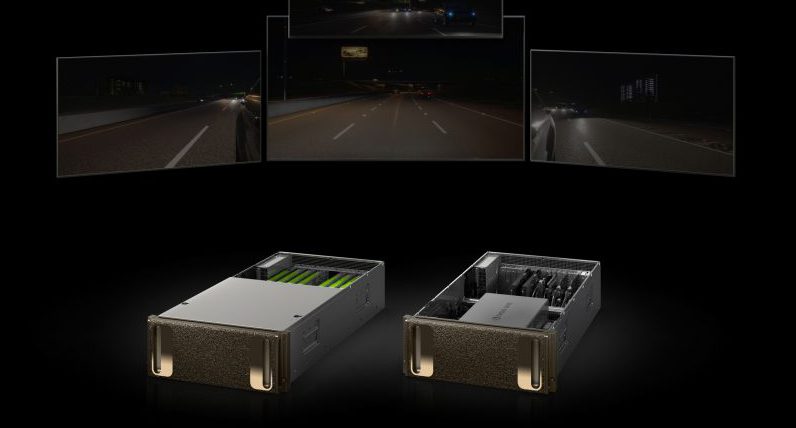
Nvidia has set up a self-driving car automation program to test out its technology and safety features. The system, called Drive Constellation, allows the company to test and validate its artificial intelligence and graphics processing through cloud-based services. The tests use photo-realistic simulations of hazards such as rainstorms, snowstorms, sun glare, and other dangerous situations to validate what its artificial intelligence would do in such a situation. The tests will check how the LiDAR, cameras, sensors, and processors work in extreme conditions.
Testing in a simulated environment may help Nvidia work out any kinks before vehicles with its chips get on real roads. According to Rob Csongor, who is the Vice President and General Manager of automotive at Nvidia, “We can increase the robustness of our algorithms … all in a fraction of the time and cost it would take to do so on physical roads.” This comes in the wake of the Uber crash in Arizona, which caused a fatality. Nvidia had self-driving cars testing on public roads in California, New Jersey, Japan, and Germany, but it has suspended the public road testing for the time being.
Strategic Partnerships for Scaling Up of the SoC
Nvidia has developed a strategic partnership with Continental, which is a vehicle supplier that has developed an artificial intelligence platform for autonomous cars. The plan is for Continental to use Nvidia’s Xavier SoC to power its artificial intelligence. Continental plans to have its platform up and running in autonomous cars by 2021. Continental plans to offer its platform to different automobile manufacturers, including those that neither have the time nor the technological expertise to build their own artificial intelligence platforms.
The goal of the partnership is to have the Xavier technology and artificial intelligence platform powering self-driving cars that have SAE Level 2 to SAE Level 5 autonomy. Nvidia has also developed strategic partnerships directly with automobile manufacturers and ride-sharing services, including Toyota, Volkswagen, Uber, Audi, Bosch, ZF, and others.
Nvidia’s Goals and Plans for the Future of Self-Driving Cars
Nvidia’s Xavier is included in the Pegasus AI computing platform, which is capable of SAE Level 5 autonomy. The SoC’s low electrical requirements could also make autonomous cars more efficient for practical purposes since the chip does not use so much power that the car’s battery would have to be recharged after a short amount of time.
This could advance the goals of auto manufacturers to get their fully autonomous vehicles onto the roads for commercial purposes such as deliveries and ride-sharing services. Nvidia’s CEO Jensen Huang believes that the self-driving cars with Xavier could be on the road by 2020. According to Huang, “I believe that everything that moves will be autonomous some day.” To that end, Nvidia plans to get robot taxis on the roads by 2019 and SAE Level 4 autonomous cars on public streets by 2020 or 2021.























[…] clindamicina precio[…]
clindamicina precio
tadalafil
tadalafil